September is Blood Cancer Awareness Month

September is Blood Cancer Awareness Month. Blood cancers include leukemias, lymphomas and multiple myeloma. There has been dramatic improvement in the treatment and outcomes for most blood cancers in the past two decades. Many of these cancers are more common as someone ages, but some leukemias and lymphomas are fairly common in children.
- Approximately every 3 minutes, one person in the US is diagnosed with leukemia, lymphoma or myeloma.
- An estimated combined total of 187,740 people in the US are expected to be diagnosed with leukemia, lymphoma or myeloma in 2024.
- New cases of leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma are expected to account for 9.4 percent of the estimated 2,001,140 new cancer cases that will be diagnosed in the US in 2024.
- An estimated 1,698,339 people in the United States (US) are living with or in remission from leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs).
- Globally, an estimated 1.24 million people are diagnosed with blood cancer each year, which is about 6% of all cancer cases.
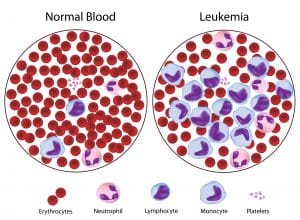 Leukemias are cancers of the white blood cells made in the bone marrow. They often present with symptoms related to suppression of normal blood production, such as fatigue from too few red blood cells or unexplained bleeding or bruising from decreased platelet production.
Leukemias are cancers of the white blood cells made in the bone marrow. They often present with symptoms related to suppression of normal blood production, such as fatigue from too few red blood cells or unexplained bleeding or bruising from decreased platelet production.
An estimated 60,650 new cases of leukemia are expected to be diagnosed in the United States in 2022, according to federal statistics. Leukemia is the most common cancer in children younger than 15 years.
There are four major types of leukemia: acute myeloid leukemia (AML), which affects myeloid cells and grows quickly; chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), which affects lymphoid cells and grows slowly; acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), which affects lymphoid cells and grows quickly; and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), which affects myeloid cells and usually grows slowly at first. AML and CLL are the most common types in adults, and ALL is the most common type in children.
Hodgkin lymphoma is usually marked by the presence of a type of cell called the Reed-Sternberg cell in the lymph nodes. Hodgkin lymphoma may also occur in patients who have acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma includes a large, diverse group of cancers of immune system cells. Scientists typically categorize them as either slow-growing or aggressive. The most common types of NHL in adults are diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. An estimated 80,470 people in the United States will be diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma in 2022, according to the National Cancer Institute.
Both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas can occur in children and adults.
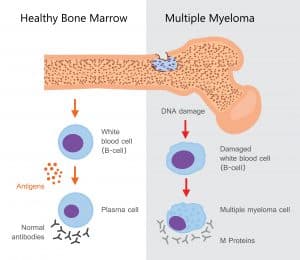
Symptoms may not be present or may be non-specific, such as loss of appetite, bone pain, and fever People may experience: Pain in the back or bones, anemia, fatigue, or loss of appetite. Also common: constipation, hypercalcemia, kidney damage, or weight loss.
l;ymphomalymphomREFERENCES:
https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.3322/caac.21834
