Exercise Plays a Crucial Role in Reducing Inflammation
 Exercise plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation, which in turn has a significant impact on cancer prevention. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury, infection, or harmful stimuli, and it is an essential part of the immune system’s defense mechanism. However, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including cancer.
Exercise plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation, which in turn has a significant impact on cancer prevention. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury, infection, or harmful stimuli, and it is an essential part of the immune system’s defense mechanism. However, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including cancer.
Here’s how exercise helps to reduce inflammation and its connection to cancer prevention:
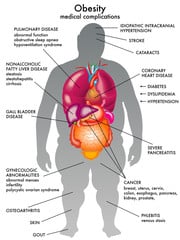 Reduces Adipose Tissue (Fat) and Obesity: Regular physical activity helps to maintain a healthy weight and reduces excess adipose tissue. Obesity is associated with chronic inflammation due to the release of inflammatory cytokines from fat cells. By decreasing adipose tissue and promoting a healthy weight, exercise can lower inflammation levels.
Reduces Adipose Tissue (Fat) and Obesity: Regular physical activity helps to maintain a healthy weight and reduces excess adipose tissue. Obesity is associated with chronic inflammation due to the release of inflammatory cytokines from fat cells. By decreasing adipose tissue and promoting a healthy weight, exercise can lower inflammation levels.
Enhances Immune Function: Exercise has a positive impact on the immune system, improving its ability to fight infections and regulate inflammation. Physical activity promotes the circulation of immune cells, increasing their surveillance and effectiveness in detecting and eliminating cancerous cells.
Regulates Inflammatory Markers: Studies have shown that exercise can help reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), while promoting the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines. This balance is crucial in preventing chronic inflammation.


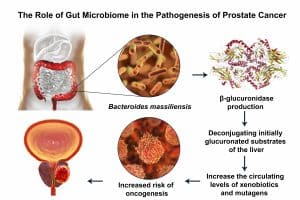
Enhances DNA Repair: Regular physical activity can improve DNA repair mechanisms in cells. Unrepaired DNA damage can lead to mutations and the development of cancer. Exercise helps maintain proper DNA repair, reducing the likelihood of cancerous growth.
Overall, exercise plays a multifaceted role in reducing inflammation and minimizing the risk of cancer development. Engaging in regular physical activity can be a valuable lifestyle choice to support overall health and cancer prevention. However, it’s essential to remember that exercise should be combined with a balanced diet and other healthy lifestyle habits for optimal benefits. Always consult with a CETI Cancer Exercise Specialist before starting a new exercise routine, especially if you have existing health conditions.
