Why is it So Difficult to Lose Weight While on Hormonal Ablation Therapy for Cancer?

Hormonal ablation therapy is commonly used in the treatment of certain types of cancer, such as prostate, testicular, breast, and ovarian cancer. This therapy aims to reduce the levels of male/female hormones in the body, as these hormones can stimulate the growth of cancer cells. While hormonal ablation therapy is effective in treating cancer, it can lead to various side effects, and weight gain is one of them.
Several factors contribute to the difficulty of losing weight on hormonal ablation therapy:
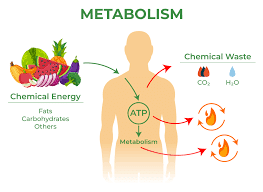 Metabolic Changes: Hormonal ablation therapy can alter the body’s metabolism, leading to changes in how the body processes and stores energy. This can result in an increase in body fat and a decrease in muscle mass, making weight loss more challenging.
Metabolic Changes: Hormonal ablation therapy can alter the body’s metabolism, leading to changes in how the body processes and stores energy. This can result in an increase in body fat and a decrease in muscle mass, making weight loss more challenging.
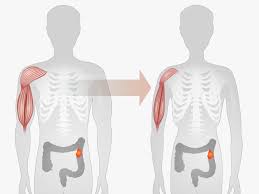
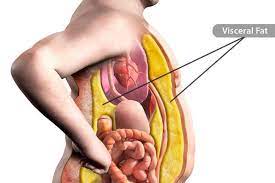



Despite these challenges, it’s important for individuals undergoing hormonal ablation therapy to focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This includes adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity (as tolerated), and seeking support from healthcare professionals, nutritionists, and mental health professionals to address both the physical and emotional aspects of weight management. Always consult with your healthcare team for personalized advice and guidance based on your specific medical situation.

