May is Melanoma and Skin Cancer Awareness Month
 Non-melanoma skin cancer:
Non-melanoma skin cancer:
Non-melanoma skin cancer is a very common cancer in the United States, with more than 5 million people diagnosed each year. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are non-melanoma skin cancers, are the most common types of skin cancer. Non-melanoma skin cancers rarely spread to other parts of the body.
Melanoma:
Melanoma is an aggressive form of skin cancer. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body than the more common forms of skin cancer.
Melanoma is more common in men than women and among individuals of fair complexion. Unusual moles, exposure to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight (such as from tanning beds) over long periods of time, and health history can affect the risk of melanoma – American Association for Cancer Research.
Less Common Skin Cancers:
1) Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare and aggressive type of skin cancer that develops in sun-exposed skin areas and has a high likelihood of spreading to other body parts.
2) Skin lymphoma, also called Cutaneous lymphoma, is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that starts in the skin.
3) Kaposi sarcoma is a type of cancer that starts in lymph or blood vessel cells and tends to appear in the mouth and as lesions on the skin, but may also develop in the lungs, liver and digestive tract.
4) Skin adnexal tumors are tumors that start in hair follicles or skin glands.
5) Sarcomas are soft tissue tumors that can begin in deep skin tissue.
 Things that put you at higher risk for getting skin cancer are called risk factors. The main risk factor for developing skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from:
Things that put you at higher risk for getting skin cancer are called risk factors. The main risk factor for developing skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from:
1) Sunlight
2) Tanning beds
3) Sun lamps
Other factors that may contribute to developing skin cancer include:
– Having a history of severe, blistering sunburns
– Having many, or unusual, moles
– Being a blond or redhead, having fair skin that easily freckles or sunburns
– Exposure to large amounts of toxic substances such as paraffin oil, coal tar and arsenic compounds
– Family history of skin cancer
– Previously being diagnosed with skin cancer
– Being older, male
– Having a weakened immune system
– Having a rare inherited condition called xeroderma pigmentosum
– People with darker complexions have a much lower risk of most types of skin cancer.
When they do develop melanoma, people with darker skin types are much more likely to have rare types of melanoma such as acral lentiginous melanoma, an aggressive type affecting the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and nail bed. Melanoma can also develop in non-sun-exposed area such as the membranes of the mouth, gastrointestinal tract and female genital tract.
The most important warning sign of skin cancer is a new spot on the skin, especially if that spot changes shape, color or size. Another potential symptom is a spot that looks different from all the others on your skin (known as the “ugly duckling sign”).
Other signs include:
– Red or pink patches with shiny, pearly-white raised edges
– Non-healing open sores that bleed or develop a crust
– Red scaly patches of skin that may bleed
– Wart-like growths with crusted surfaces
– Hard, waxy skin lumps with visible blood cells
– A newly itchy, tender or painful sore

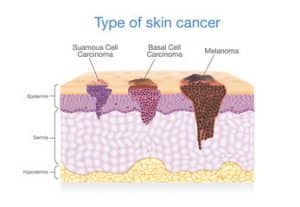 Non-melanoma skin cancer:
Non-melanoma skin cancer: Things that put you at higher risk for getting skin cancer are called risk factors. The main risk factor for developing skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from:
Things that put you at higher risk for getting skin cancer are called risk factors. The main risk factor for developing skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from: